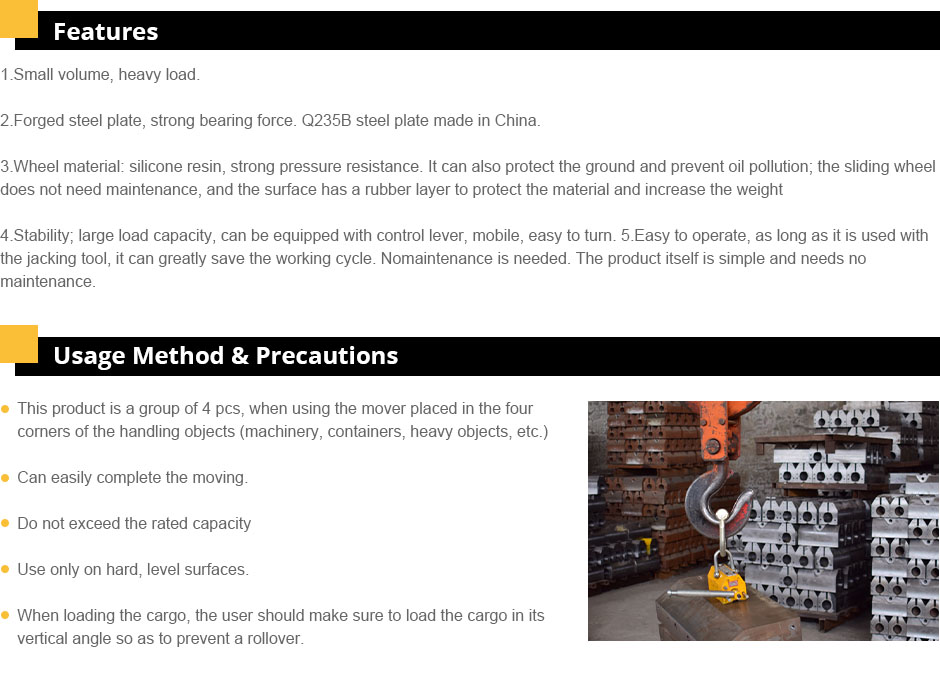
Cost Analysis for transporting Heavy Machinery and Equipment Efficiently
The Cost to Move Heavy Equipment A Comprehensive Overview
Moving heavy equipment is a critical process in various industries, including construction, mining, and manufacturing. As projects grow in scale and complexity, the need for relocating heavy machinery becomes increasingly common. However, the cost to move heavy equipment can be substantial, influenced by numerous factors such as the type of equipment, distance of transport, methodology, and geographical location. This article delves into these key aspects, providing a clear understanding of what contributes to the overall costs.
Understanding the Factors Influencing Cost
1. Type of Equipment The first major factor affecting the cost is the type of heavy equipment being moved. Construction machinery such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes vary significantly in size, weight, and disassembly requirements. Specialized equipment, like oversized loads or hazardous materials, can incur additional costs related to safety measures and compliance with transport regulations.
2. Distance of Transport The distance between the original and destination sites plays a crucial role. Longer distances typically increase transportation costs—fuel consumption, driver time, and possible overnight accommodations for the crew all add up. It’s also worth noting that moving equipment across state lines or internationally may involve additional fees due to regulatory requirements.
3. Method of Transport The methodology used for transporting the equipment significantly impacts costs. Options can include flatbed trucks, specialized transport trailers, or even barges for waterway transport. Each method entails different rental fees, labor costs, and transport times. For instance, using a lowboy trailer for oversized loads will be more expensive than a standard flatbed but necessary to comply with height and weight limits.
4. Labor and Expertise The cost of labor cannot be overlooked. Skilled professionals are required to properly disassemble, load, and unload heavy equipment. Additionally, specialized rigging services may be needed for particularly large or complex machines. Labor costs vary depending on the local market rate, the level of expertise required, and the duration of the job.
5. Insurance and Permits Heavy equipment transport often necessitates insurance to cover potential damages during transit, which can add another layer of expense. Moreover, some jurisdictions require special permits for oversized loads, which typically entail application fees and compliance checks. Understanding local regulations is crucial to avoid fines and ensure smooth transport.
cost to move heavy equipment
Planning and Budgeting for Moving Costs
Given the multifaceted nature of transporting heavy equipment, careful planning and budgeting are essential to manage costs effectively
. Here are a few strategies- Get Multiple Quotes Engaging several transport companies can help you compare costs and services. Ensure that each quote outlines what is included, enabling you to make informed decisions.
- Assess Equipment Condition If equipment requires repairs or maintenance before moving, addressing these issues in advance can help avoid unexpected costs during transit.
- Plan for Downtime Consider potential delays in transport schedules and plan project timelines accordingly to mitigate downtime costs.
- Utilize Technology Many companies leverage technology to optimize routing and logistics, potentially reducing transport time and fuel costs.
Conclusion
In summary, the cost to move heavy equipment can vary widely based on a range of factors, including the type of equipment, distance, transportation method, labor, and regulatory requirements. By understanding these factors and engaging in careful planning, businesses can manage their expenses while ensuring that their heavy machinery is transported safely and efficiently. Ultimately, investing time and resources into this process can lead to smoother operational workflows and minimize disruptions to project timelines.
-
Unlock Seamless Relocation with Our Heavy Equipment Moving ExpertiseNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unleash Unrivaled Flexibility with Our Adjustable Gantry CraneNewsJun.06,2025
-
Unleash Heavy-Duty Efficiency with Our Industrial Gantry Crane SolutionsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Revolutionize Steel Handling with Our Magnetic Lifter RangeNewsJun.06,2025
-
Master Equipment Mobility with Premium Machinery Mover SolutionsNewsJun.06,2025
-
Elevate Your Material Handling with Magnetic Lifter TechnologyNewsJun.06,2025
-
YS Permanent Lifting Magnets: The Smarter Way to Handle SteelNewsMay.22,2025
